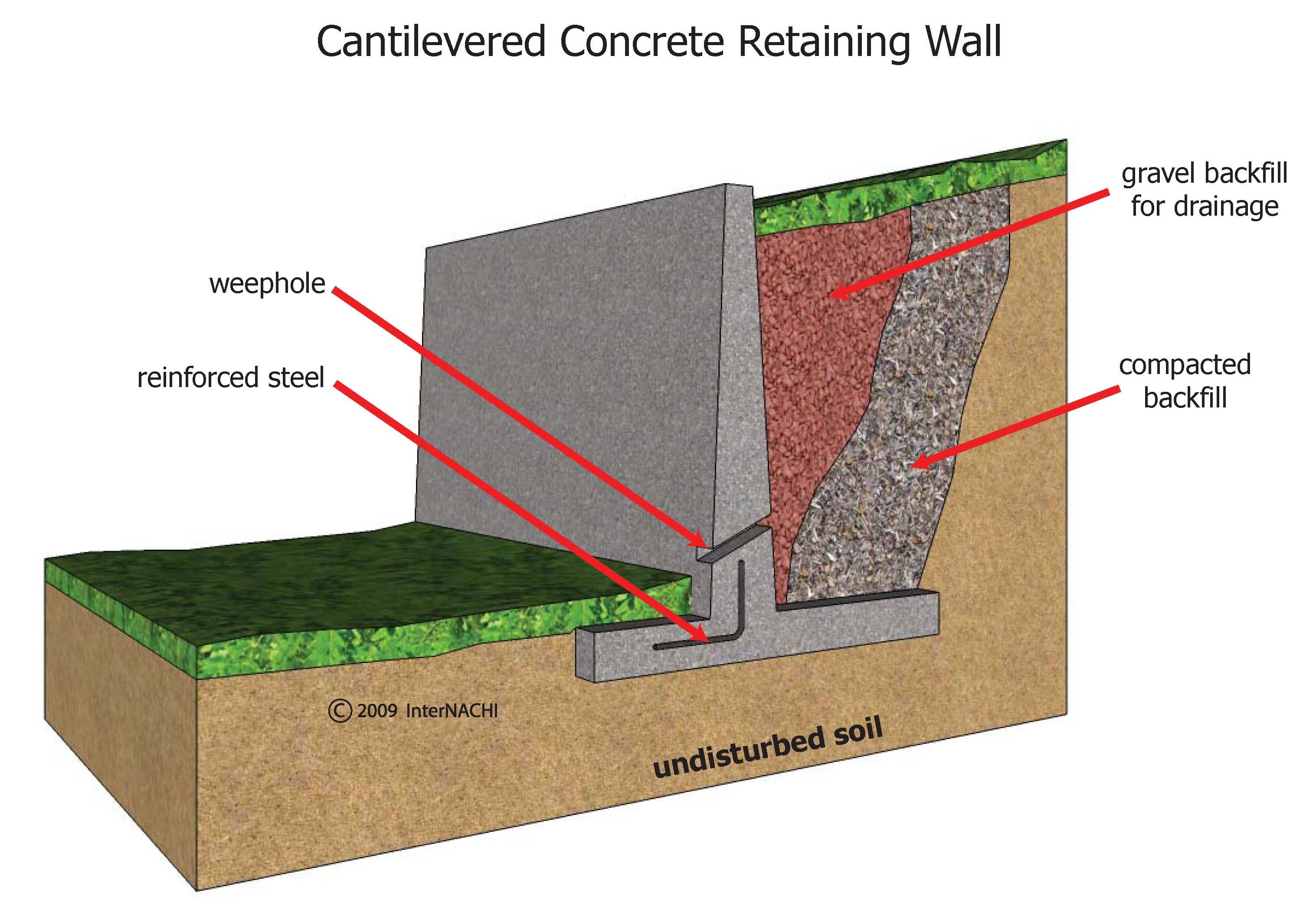
InterNACHI Inspection Graphics Library Exterior » General » cantileveredretainingwall.jpg
This Example will teach you EVERYTHING about concrete cantilever retaining wall structures! part 1 goes over problem parameters and over turning moment check.

Cantilever Retaining Wall Design MaxumStone
Cantilever walls are reinforced concrete and have an L-shaped or inverted T-shaped base. The vertical tension behind the wall is transmitted to the foundation, preventing it from collapsing as a result of lateral earth pressure from the same soil mass. A T-shaped foundation also benefits from the weight of the earth (and hence vertical tension.

Crosssection of a typical cantilever retaining wall. Download Scientific Diagram
Cantilever concrete retaining walls are commonly used for residential purposes, often as integral basement walls. Usually the cantilever wall stem is of concrete block construction rising from an in-situ concrete foundation. The following worked example is for a free-standing cantilever wall that is considered
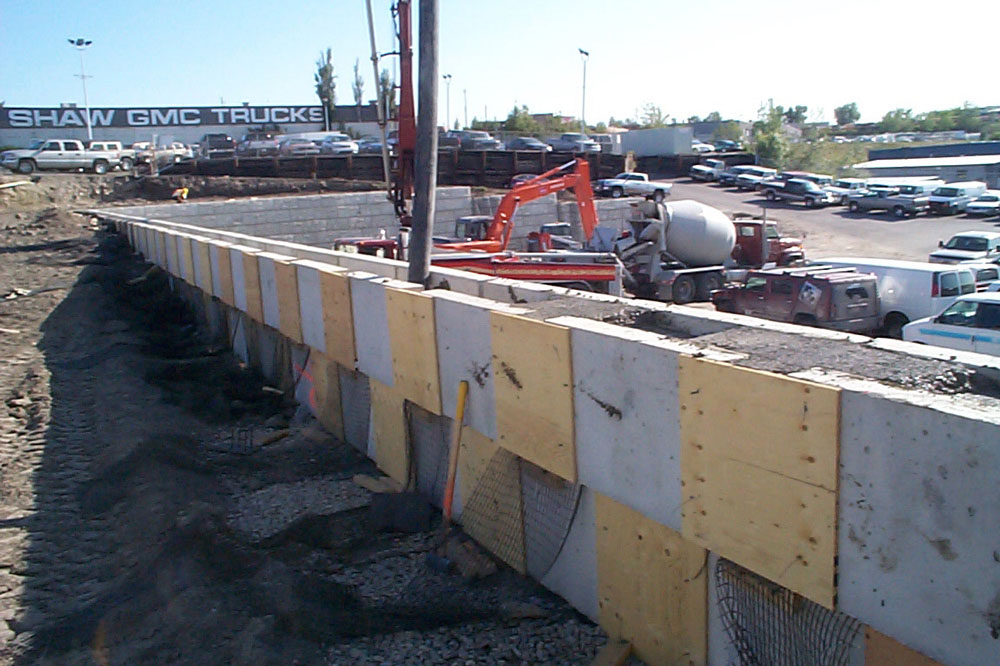

Cantilever Retaining Wall Design MaxumStone
Recommended stem designs for reinforced cantilever retaining walls with no surcharge are contained in Tables 1 and 2 for allowable stress design and strength design, respectively. These design methods are discussed in detail in Allowable Stress Design of Concrete Masonry, TEK 14-7A, and Strength Design of Concrete Masonry, TEK 14-4A (refs. 5, 6
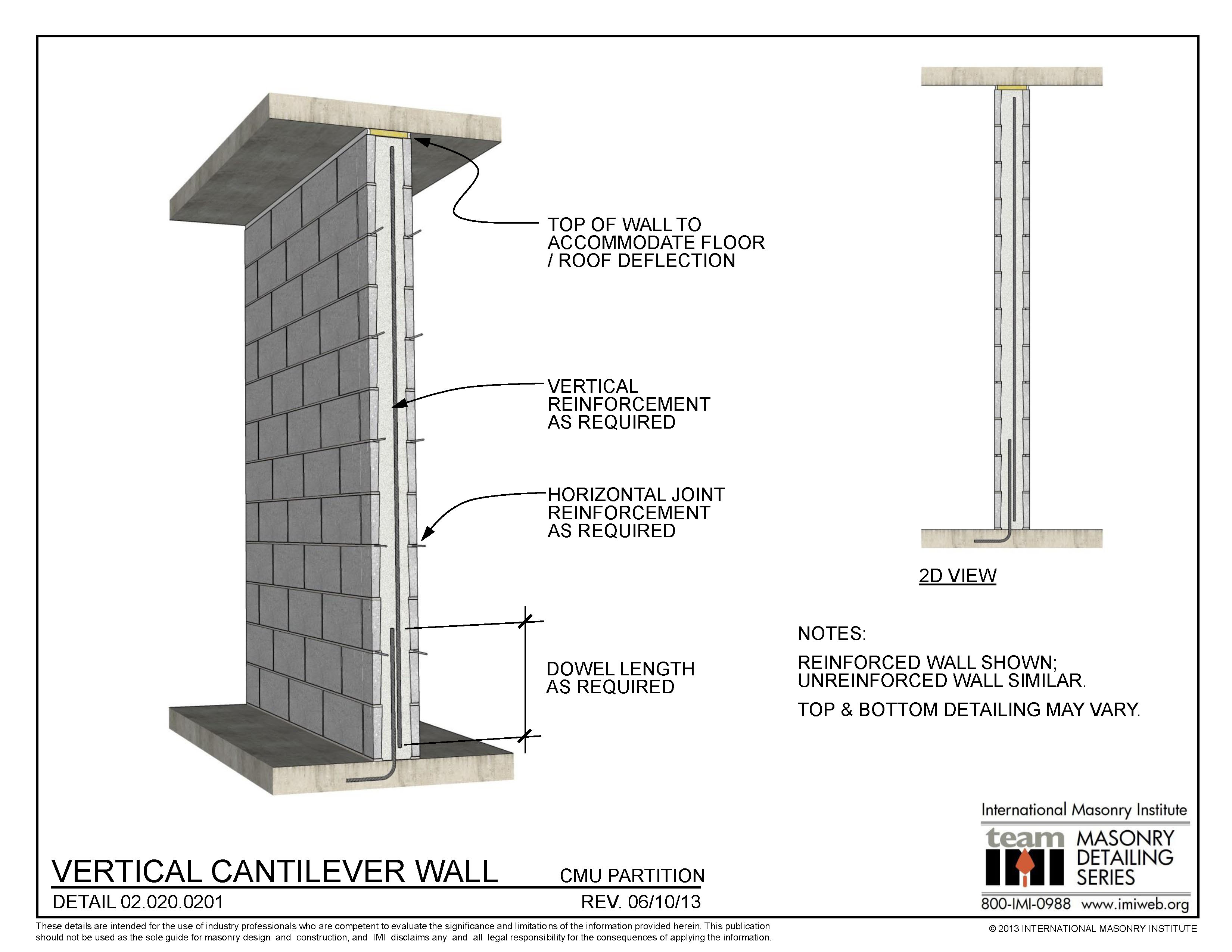
02.020.0201 Vertical Cantilever Wall International Masonry Institute
Cantilever retaining walls. Cantilever walls are built using reinforced concrete, with an L-shaped, or inverted T-shaped, foundation. This kind of retaining wall consists of a stem and a base slab (or footing) which sits under the backfill. The vertical stress behind the wall is transferred onto the foundation, preventing toppling due to.
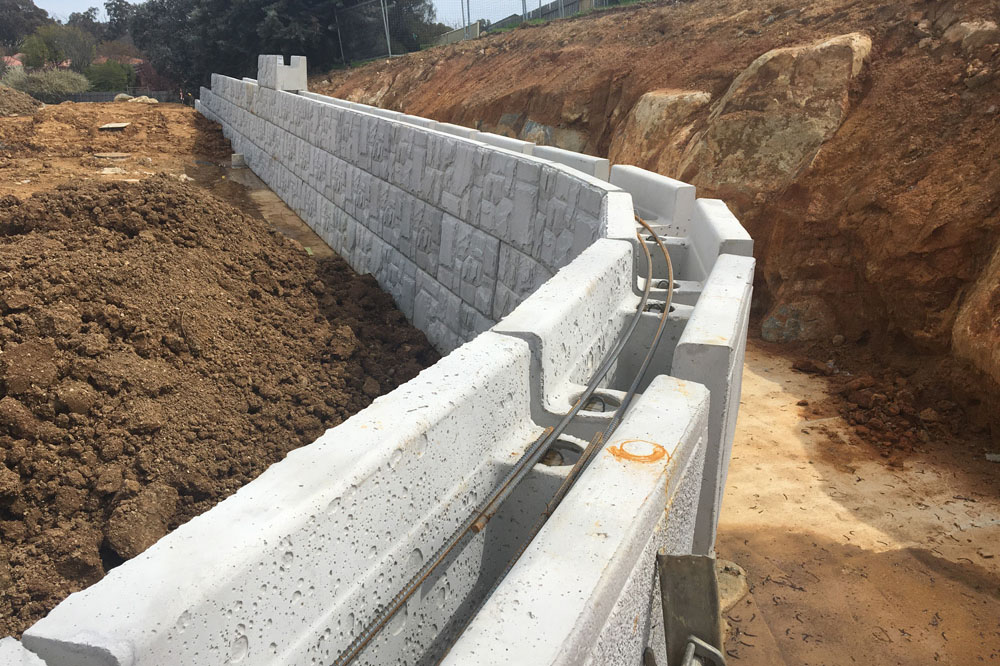

Cantilever Retaining Wall Design MaxumStone
Reinforced concrete cantilever retaining walls consist of a relatively thin stem and a base slab. The stem may have constant thickness along the length or may be tapered based on economic and construction criteria. The base is divided into two parts, the heel and toe. The heel is the part of the base under the backfill.

What is Cantilever Retaining Wall? Purpose of Cantilever Retaining wall. Different types of
Reinforced concrete cantilever retaining walls consist of a relatively thin stem and a base slab. The stem may have constant thickness along the length or may be tapered based on economic and construction criteria. The base is divided into two parts, the heel and toe. The heel is the part of the base under the backfill.

Cantilever and Restrained Retaining Wall Design Software SoilStructure Software
Cantilever retaining wall is the most common type used as retaining walls. Cantilever retaining wall is either constructed on site or prefabricated offsite i.e. precast. The portion of the base slab beneath backfill material is termed as heel, and the other part is called toe. Cantilever retaining wall is economical up to height of 10m.
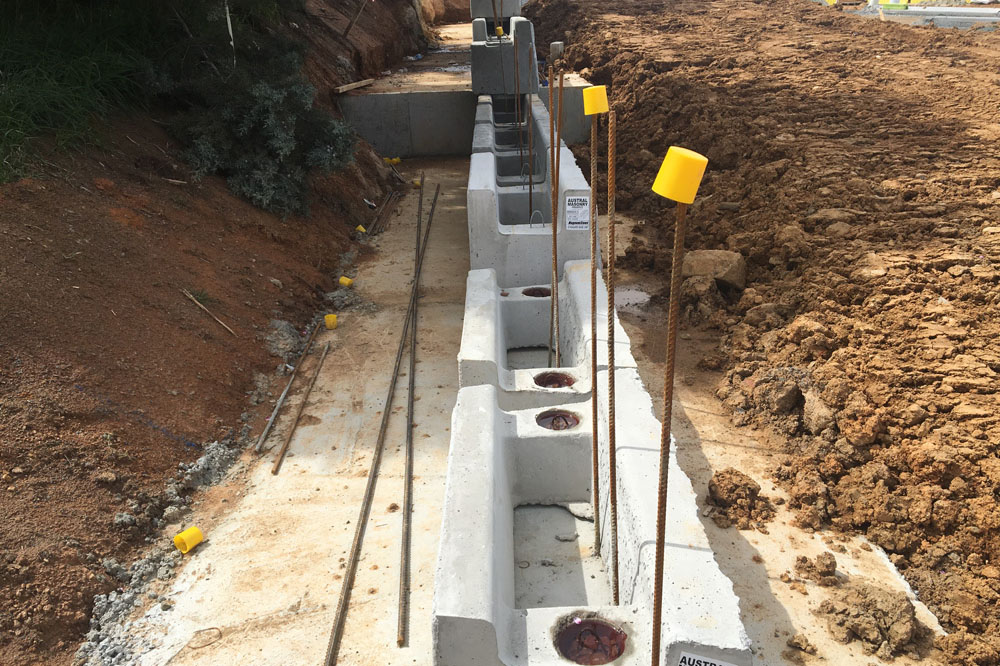
Cantilever Retaining Wall Design MaxumStone
Cantilever retaining wall are usually of reinforced concrete and work on the principles of leverage. It has much thinner stem and utilize the weight of the backfill soil to provide most of the resistance to sliding and overturning. Cantilever retaining wall is the most common type of earth-retaining structure.

Cantilever Retaining Walls
Cantilever retaining wall designs are typically selected and implemented when geogrid and gravity retaining walls are unable to meet the necessary structural criteria. This can be due to a variety of reasons, including right right-of-ways (ROWs) or sites with structures that have extremely close or limited excavation areas.

Cantilever Retaining Wall Design MaxumStone
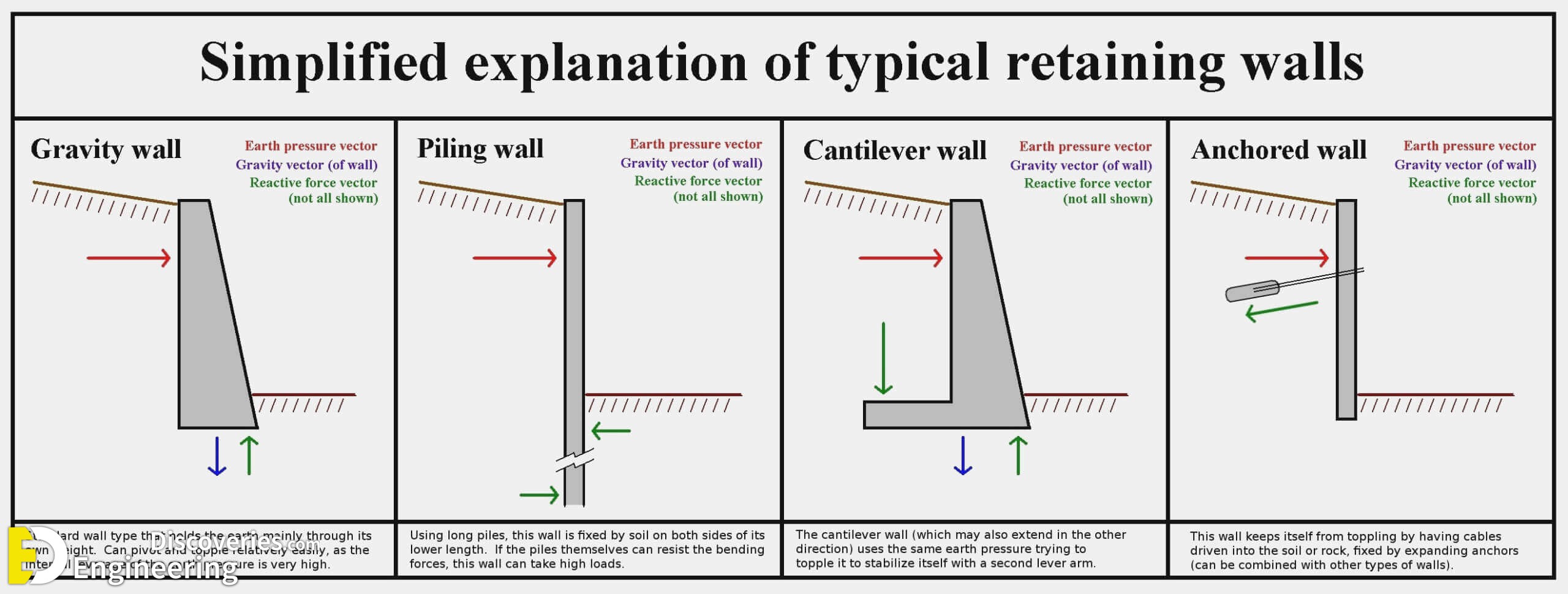
Cantilever Retaining Wall. Cantilever Retaining Walls are pretty similar to Gravity Retaining Walls, however they include an additional base component that provides additional restraint against overturning and sliding given this additional concrete. This shape is more effective to resist the active forces, as the weight of the active force.
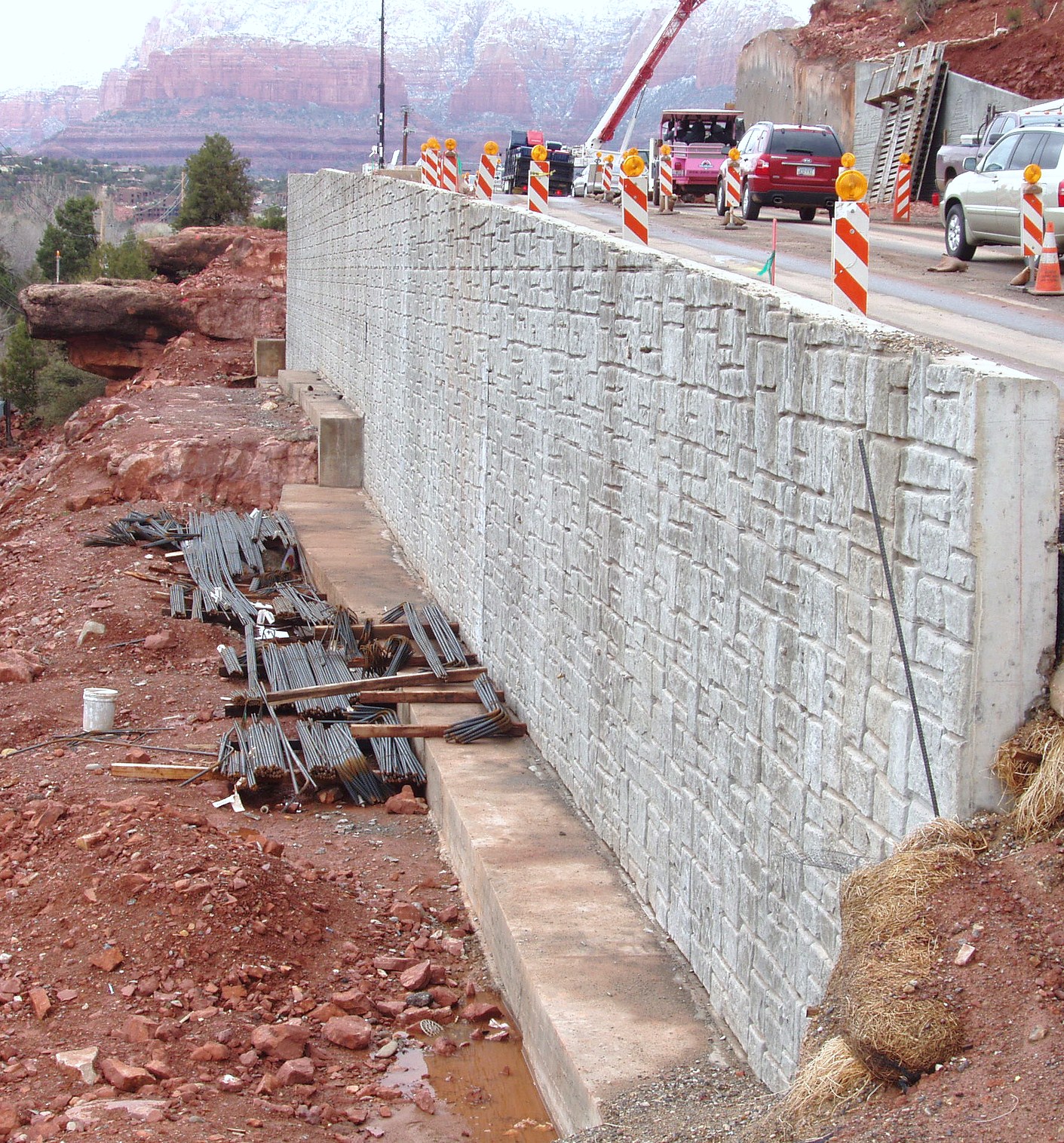

Cantilever and Restrained Retaining Wall Design Software SoilStructure Software
Cantilever retaining walls are structures that must be designed considering the different stability failure modes. The reinforcement of the wall components must provide adequate structural strength at every point of the structure. ASDIP RETAIN includes the design of cantilever retaining walls, with multiple options to optimize the design easily.

Cantilever retaining wall with relief shelves in Hyderabad, India Scientific Image
5.3 Wall 5-1 5.4 Base 5-2 5.5 Key 5-3 Chapter 6 Tabulated Designs 6-1 6.1 General 6-1 Chapter 7 Use of Tabulated Designs 7-1 7.1 Example 1 7-1 7.2 Example 2 7-1 Chapter 8 Manual Examples 8-1. Design Guide for Cantilevered Retaining Walls Author: CRSI Created Date:

Cantilever Retaining Wall Construction for Wellington Residents
Cantilever retaining walls have been widely used in construction for decades and have proven to be a versatile and efficient solution for stabilizing earth. This type of retaining wall is designed to resist lateral pressure from retained soil, creating a transition between two different levels of ground. With its unique design and engineering.
RCC Retaining Wall (Cantilever Type) Excel Sheet Engineering Discoveries
Figure A.1-Retaining Wall Cross Section. Consider the cantilever retaining wall with the cross-section shown in the above Figure A.1, which retains a 2m depth of soil having the groundwater table at -1.0m level. Design Parameters: Soil Bearing Capacity, q all : 100 kPa; Coefficient of Soil Friction, ф: 30° Unit Weight of Soil, ɣ s: 18 kN/m 3

dfdfdfd Complete Design of Cantilever Retaining Wall [pdf]
Parts of Cantilever retaining wall. Stem: It is the vertical upright portion of the cantilever wall which supports or restrain the lateral confinement. The stem has a greater slender ratio. Sometimes the stem is made of the same thickness throughout and sometimes they are made thicker at the base. Toe: it is the base footing embedded on the.